- This event has passed.
21st June – BioBriefing – Biocontainment Capability for Biotech
June 21, 2016 @ 8:45 am - 10:30 am AEST
Event Navigation
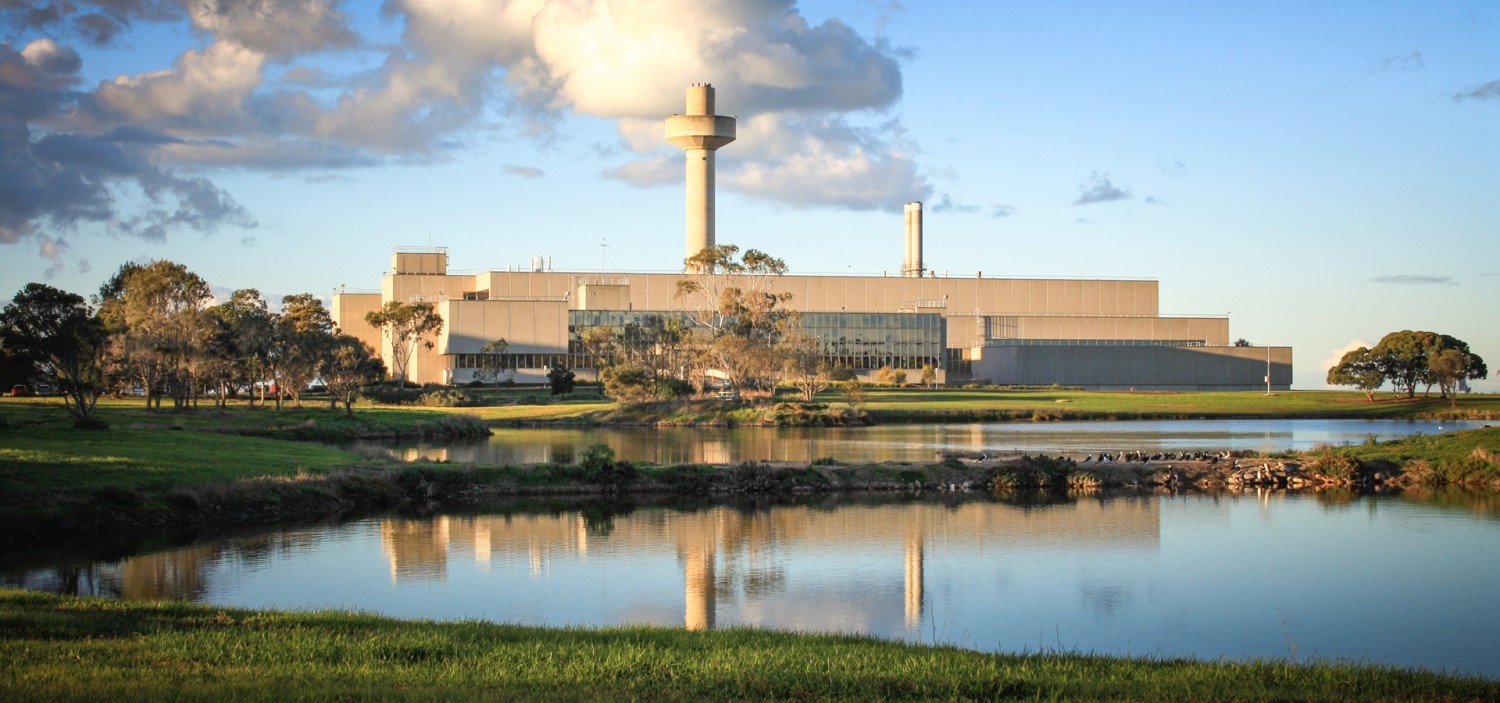

BioMelbourne Network with the CSIRO Australian Animal Health Laboratory present: Biocontainment Capability for Biotech
The CSIRO Australian Animal Health Laboratory (AAHL) helps protect Australia’s multi-billion dollar livestock and aquaculture industries, and the general public from emerging infectious disease threats. It is a biocontainment facility enabling research on high-consequence pathogens including comparative pathogenesis and offering unique pre-clinical testing capability.
With the increased global threat from emerging infectious diseases and pandemics, Victoria is well positioned to be a leading global hub in this critical area of unmet need. This event will highlight the unique capabilities that support research and product development in this space and explore the infrastructure that enables work with dangerous pathogens such as Ebola, Zika and influenza.
Introduction – Dr Kurt Zuelke, Director, AAHL
Virtual Tour – Sally Corinaldi, Stakeholder Engagement & Marketing Manager, AAHL
Presentation – Animal Models for High Consequence Pathogens – Dr Glenn Marsh, Research Scientist & Team Leader Molecular Virology, AAHL
Date: Tuesday, 21st June
Time: Registration from 8:45am for a 9:00am – 10:30am presentation followed by a networking session.
Venue:
Lecture Theatre
CSIRO Australian Animal Health Laboratory
Corner Portarlington and Boundary Roads
Geelong East, 3219
Price:
Members – $65
Non-Members – $110
(Prices include GST)
To check if your organisation is a member click here
Introducing the Guest Speakers:
 Dr Kurt Zuelke, Director, CSIRO AAHL
Dr Kurt Zuelke, Director, CSIRO AAHL
Previously Dr Zuelke was the Director of the USDA Agricultural Research Service’s National Animal Disease Center (NADC) from 2006 to 2012. Located in Ames Iowa, the NADC is the largest US federal animal health research facility focused on high impact endemic diseases of livestock and wildlife species.
While at NADC, Dr Zuelke led NADC’s strategic business reorganisation and relocation into new $470M state-of-the-art facilities that support large-scale BSL-2, BSL-3 and BSL-3Ag level research in livestock and wildlife species. Dr Zuelke co-founded the USDA National Centers for Animal Health (NCAH), and served on the NCAH Board of Directors in conjunction with Directors of the USDA APHIS National Veterinary Services Laboratory (NVSL), and USDA APHIS Center for Veterinary Biologics (CVB).
From 1995 to 2001, Dr Zuelke was with the Victoria Department of Primary Industries in Melbourne, Australia where he led industry and government-sponsored research performing functional genomics and biotechnology research in dairy cattle and native Australia wildlife species. Partnering with industry and university researchers, Dr Zuelke’s team produced the first transgenic cloned calf in Australia.
From 2005 to 2006, Dr Zuelke served as the USDA’s representative in President Bush’s Office of Science and Technology Policy where he coordinated federal, agricultural, biotechnology and life science research and policy issues, and led the US delegation to the OECD Working Party on Biotechnology.
 Dr Glenn Marsh, Research Scientist, CSIRO AAHL
Dr Glenn Marsh, Research Scientist, CSIRO AAHL
Dr Marsh is currently a Research scientist and Team leader for molecular virology. Glenn is trained to work at the highest levels of biocontainment. His research is focused on pathogen discovery/characterisation and the molecular determinants of pathogenicity. For the past several years Glenn’s focus has been on paramyxoviruses from bats. Glenn has worked with Hendra and Nipah viruses, with a goal of his research being to understand why this virus is so deadly compared to other paramyxoviruses.
In addition to paramyxoviruses, Glenn’s other area of research is the filoviruses. This work started with testing of an Ebola Reston virus isolate from the Philippines in its ability to cause disease in pigs. This work is now investigating the basis of differences in the ability of these viruses to cause disease in humans.
 Sally Corinaldi, Stakeholder Engagement and Marketing Manager, CSIRO AAHL
Sally Corinaldi, Stakeholder Engagement and Marketing Manager, CSIRO AAHL
Sally has 25 years’ experience in strategic marketing management roles, predominately in the public health and vaccines market both in Australia and Europe. Since joining CSIRO, her interest in infectious diseases has continued and expanded to include emergency animal diseases as well as zoonotic diseases – infectious diseases affecting people that are of animal origin.




